Supplements May Be Helpful for COVID-19
Those of us in the integrative medicine field have long seen the benefits of supplements and herbal medicine in healthcare.
COVID-19 is a novel virus, meaning it has never been seen before in nature. There is a lot that we don’t know about this virus, but there is a lot that we are learning as well. There have been studies done with supplements for other types of coronaviruses like SARS CoV. We also have research about the effects of supplements on the immune system suggesting that they may be helpful for upper respiratory infections in general.
Below is a list of several supplements along with a short discussion on research and clinical experience and references where you can read more on each topic. Please note: None of these have been proven as treatments for COVID-19, and none of the information should be taken as medical advice.
- Antioxidants
- Vitamin C
- Glutathione
- NAC
- Quercetin
- Anti-Viral Properties
- Chinese Herbal Med.
- Monolaurin
- Biofilm disruptors
- Quercetin
- Immune Support
- Probiotics
- Zinc/Copper
- Vitamin D
- Melatonin
Dietary supplements are generally considered safe, but it’s important to review your medical history and current medications with a practitioner before starting. Please call (703) 532-4892 to make an appointment with your provider, nutritionist, or acupuncturist/herbalist. If you suspect you have any kind of infection, please make a telemedicine/ cloud appointment with your doctor.
Please remember that supplements are not regulated by the FDA and sometimes do not contain ingredients that they claim. At The Kaplan Center, we do extensive research to find the best companies with 3rd party testing to make sure you get the highest quality products. You can order your supplements directly through our online store at: https://store.kaplanclinic.com/
It is important to continue following guidelines from health departments and governments including frequently washing hands for 20 seconds, staying physically distant and socially innovative. When in public places like grocery stores, be sure to wear a mask.
ANTIOXIDANTS
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is long known for helping the immune system prevent colds and flu. It is important for the function of white blood cells to fight infections and the overall immune system. High dose Vitamin C is being used by IV in several hospitals around the world including in New York. There is a small study that showed critically ill patients with COVID-19 who were given 1-6 g of Vitamin C either intravenous (IV) or oral decreased ventilation time by 25%. There are other trials in progress to see if high dose Vitamin C can improve outcomes. Doses range in 12-24g administered by IV. At this time there is no evidence that taking Vitamin C orally will prevent or cure COVID-19. As a supplement, it is suggested to take 3g of Vitamin C per day. Talk to your doctor about if IVs would be right for you.
Glutathione/NAC
Glutathione is a powerful antioxidant in the body. It scavenges damaging free radicals and is involved in tissue repair and builds chemicals and proteins that are used for the immune system. N-Acetyl cysteine, or NAC, promotes the production of glutathione and is also used as a supplement. Studies in animal models of other viral infections have shown that NAC reduced the severity and duration of symptoms by increasing cellular defense and repair. NAC is taken in doses of 500-600mg. Glutathione can be taken orally 500mg or by IV 400-2400 mg with a doctor’s order.
Quercetin
Quercetin is a bioflavonoid found in a variety of fruits and vegetables. Laboratory and animal studies have shown that quercetin may inhibit a wide variety of viruses, including a coronavirus SARS CoV which is related to COVID-19. Quercetin supports antioxidant capacity and protects lung tissue. As a supplement is combined with Vitamin C, bromelain or sold as a single supplement. Recommendation is between 500mg-1000mg daily.
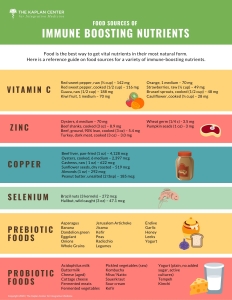
Food Sources: Leafy green vegetables, dill, peppers, apples, grapes, fennel leaf, red onion, oregano, chili pepper, green tea, and black tea.
ANTI-VIRAL PROPERTIES
Chinese Medicine
Computer analysis done in February of this year showed which drugs and natural compounds have the potential to inhibit COVID-19. Several Chinese herbs were shown to have the potential to interact with specific targets of SARS-CoV-2. These included Andrographis paniculate and Scutellaria baicalensis, two herbs that are commonly used in formulas for upper respiratory infections. This data is preliminary and does not meet the standards of evidence-based medicine.
Chinese herbal medicine is a complex system of medicine that is based on sequential diagnoses of signs and symptoms that change throughout the illness. It is personalized and a formula should be prescribed by an NCCAOM certified herbalist.
Monolaurin
Generally considered anti-viral, coconut oil contains lauric acid and the derivative monolaurin. It prevents the adherence of viruses to tissues by fluidizing the lipids and phospholipids in the envelope surrounding the virus that leads to the disintegration of viral particles and symptom improvement. Studies have not been conducted in humans on coronaviruses. Unrefined coconut oil contains the most lauric acid. Refined coconut oils and MCT oils contain very little. Supplementation of monolaurin is 1,200 -1,800 mg 2-3 times per day.
Biofilm Disruptors
Biofilm disruptors are enzymes that have the ability to weaken the virus by inactivating or fluidizing its outer layer, then exposing its viral content to the immune system. Biofilm disruptors are extensively studied for the treatment of bacterial infections, as most bacteria protect themselves within biofilms to hide away from antibacterial therapies. They slowly multiply until they form important colonies that then attack the body’s immune defense. An example of a biofilm disruptor is Lumbrokinase found in Buluoke, made from earthworms.
Probiotics
Are friendly bacteria that reside in the intestinal tract, they actively participate in the modulation of the immune system, synthesize vitamins, and aid digestion. Studies have shown that probiotic use can decrease the number of respiratory infections, particularly in children. Food sources include fermented foods like sauerkraut, kefir, yogurt, kombucha, kimchi, natto, and tempeh. We can’t overstate the importance of gut health and nutrition on the immune system. For that reason, look for an entire article on this subject in a future newsletter.
IMMUNE BOOSTERS
Zinc/Copper
Zinc may improve the chance of avoiding respiratory tract infections in the elderly and those who are zinc deficient and is shown to have strong anti-viral properties. It is found in beef, crab, lobster, and smaller amounts in chicken, cheese, kidney beans, garbanzo beans, cashews, and almonds. Supplementation can be taken in a pill or lozenge, daily recommendation is between 30-60mg.
Copper is a trace mineral that is needed in small amounts. It also has immune-boosting properties. The problem with supplementation of trace minerals is that they compete for absorption, so it’s necessary to take about 8 mg of copper along with Zinc. Typically a multivitamin supplement contains a small amount of copper for this reason. Be sure to eat food sources like two squares of 80% dark chocolate!
Food Sources of Immune-Boosting Nutrients
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is created in the body in response to sunlight. While vitamin D has not been studied for coronavirus, low Vitamin D levels have been linked to a higher risk of upper respiratory infections in general. Most people do not have optimal levels of Vitamin D, especially in the winter. Since it is not found in foods at doses needed, supplementation is recommended at 2,000-5,000 IU per day.
Melatonin
Melatonin is used as a sleep aid that also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Melatonin also has been shown to have an inhibitory effect on NLRP3 inflammasomes, which COVID-19 stimulates to create a cytokine storm in the late stage of the disease. This compelling research suggests the potential for melatonin as adjuvant treatment for COVID-19 but more research is needed. Dosage is typically 5-20 mg at bedtime.
Sources/ Additional reading:
Vitamin C:
https://jintensivecare.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40560-020-0432-y
NAC/Glutathione:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0033062020300372?via%3Dihub
Chinese herbs:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211383520302999
Monolaurin:
Seleem, D., Freitas-Blanco, V.S., Noguti, J., Zancope, B.R., Pardi, V., & Murata, R.M. (2018). In Vivo Antifungal Activity of Monolaurin against Candida albicans Biofilms. Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin., 41(8), 1299-1302. doi:10.1248/bpb.b18-00256
https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/act.2006.12.310?journalCode=act
Melatonin:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024320520303313?via%3Dihub
http://www.melatonin-research.net/index.php/MR/article/view/71
We are here for you, and we want to help.
Our goal is to return you to optimal health as soon as possible. To schedule an appointment please call: 703-532-4892 x2










Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!